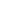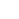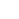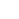LOT 475 Medieval 'Boar Hunting' Sword
Viewed 971 Frequency
Pre-bid 0 Frequency
 Collect
Collect
Name
Size
Description
Translation provided by Youdao
Circa 1475-1480 AD. A hunting sword, dedicated to the hunt of boar and deer; on the shelled square an inlaid image of a boar (?); the point, shaped as a long facetted leaf with traces of gilding, fitted in the middle with a fuller, and showing a hole which possibly had two metallic wings attached, destined to stop the penetration of the blade inside the body of the hunted beast; the tang still covered by wooden grip, the pommel pear-shaped, while the cross-guard is straight having a central thickness for the passage of the tang. See Scalini, M., ,i>A bon droit, spade di uomini liberi, cavalieri e santi, Milano, 2007; Abbott, P., Armi: storia, tecnologia, evoluzione dalla preistoria a oggi, Milano, 2007. 1.5 kg,1.22m (48"). From an important private family collection of arms and armour; acquired on the European art market in the 1980s, and thence by descent; believed originally from Liege, Belgium; accompanied by an academic report by military specialist Dr Raffaele D'Amato. This hunting sword is a good parallel to the famous hunting sword of King Renate d'Anjou (Scalini, 2007, p.206, cat.48), also with inlaid blade with scenes of hunters playing the horn, and various animals. Some parallel is visible also with a hunting boar sword, of Germanic origin, with triangular blade and flamed tip, fitted originally with a leather grip hilt. This kind of swords were held with a hand and half, acting as a hunting spike. The hunting boar sword (German Sauschwert) appeared at the end of the 15th century, and had in contrast to a conventional sword or hunting sword, a four-edged blade, which was flattened and ground at the bottom. At the upper end of this ground blade, there were usually two downwardly bent spikes, which prevented a too deep penetration of the blade into the body of the beast and thus keep the hunter at a safe distance. The handles correspond approximately to the shapes of the usual war swords. Except for the characteristic cutting edge and stopper attached to the blade, this special kind of sword looked similar to Estock. In fact, the boar sword was mainly based on the Estock or tuck, its broad stiffened blade being designed to withstand the power of the charging boar or other large animal. The cutting edge was a double-edged blade, and its shape was often expressed as a 'leaf-shaped' or 'ear-blade-shaped', a part wider than the blade to improve the wounding and killing of the wild boar. The longer body of the sword was not sharpened like the blade of a usual sword: being dedicated to piercing the beast's flesh, it did not require a blade for cutting, also to avoid the risk of wounding of the user. The blade was a hard rod that could withstand the boar's rush, and its cross-section was circular or polygonal, like in our specimen. Many grips were long enough to allow the weapon to be gripped with both hands. From the horse it could be used with one hand, but presence of the stopper and the length of the grip suggest that often it was used with both hands also from horseback. At the beginning of the sixteenth century, the shape of these swords was soon transformed by Italian influence, as the blades became shorter and lighter, finally becoming the hunting knife of the 17th century. Most probably our specimen is from a palace or a private household. The piece is very rare and in excellent condition. Introduced in 14th century, this special type of hunting sword was mainly used for wild boar hunting. By around 1500 it had developed its main characteristic, i.e. the facetted or leaf-shaped spear point, to which was later added, near the end of the blade, the crossbar to prevent the animal running up the length of the blade and so making difficult to retrieve. The crossbar was attached between the cutting edge and the blade to prevent the boar being pierced too deeply by the sword. If the sword stabbed deeply, there was the risk that the wild boar could have stabbed the sword's handler with a fang, and it would have been difficult to remove the sword from the boar's body after. It was necessary to devise measures so that the stopper would not get in the way when placed in the sheath. Unlike a detachable crossbar, some specimens have a rod-shaped stopper that was fixed to the blade with a mechanism that allowed the sword to be fit in the sheath. Specimens of such swords that could be rotated and spread existed, or a fold-able spring loaded with a stopper that automatically expanded when the sword was removed from the sheath. In addition to these rod-shaped stoppers, there were also disk-shaped stoppers, as seen in the hunting spears since the Roman age. While noblemen led the boar-hunt from the horse, using such weapon, the hunters, who belonged to the hunting party, often preferred the so-called winged spear, a spear-like pole-arm fitted with two wings lateral at the blades. Until around 1470, the Burgundian fashion was to hunt, by employing longer, specially shaped swords 'Gjaidschwerter'. Hunting swords from the time of Emperor Maximilian I (1508-1519) have the usual grip of swords to one and a half hand, without German-style fist-guard. Sometimes the pommel had a beak-like shape. The blade was always single-edged with an average length of 85 cm. The hunting party of the German Holy Emperor was composed by a special team, dressed with red coats, low caps and armed with such weapons, deputed to join the Emperor in the boar hunting.
Preview:
Monday 25th November from 12 noon Champagne Reception 6pm - 9pm
Address:
23-24 Berkeley Square London, W1J 6HE United Kingdom
Start time:

Online payment is available,
You will be qualified after paid the deposit!

Online payment is available for this session.

Bidding for buyers is available,
please call us for further information. Our hot line is400-010-3636 !

This session is a live auction,
available for online bidding and reserved bidding