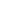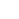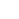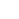LOT 477 Medieval Ilkhanid Iron-Handled Mace
Viewed 206 Frequency
Pre-bid 0 Frequency
 Collect
Collect
Name
Size
Description
Translation provided by Youdao
Circa 1330 AD. A heavy iron war mace, with hexagonal prismatic head surmounted by an iron button, the faces of the hexagon divided by lines preserving traces of gilding; mounted upon an iron staff with traces of silver, characterised by a ring of entanglement at the top and three concentric circles below. See ??????? ?.?. ???????-????????? ?????????? ?????? ???????? XIV - ?????? XV ??. // ??????????? ????? ? ??????? ? ???????? ????? ??????, ?., 1983; Head, 1984, Armies of the Middle Ages, volume 2, Worthing, 1984; Nicolle, D. Arms and Armour of the Crusading Era, 1050-1350, Islam, Eastern Europe and Asia, London 1999; Bashir, M. (ed.), The Arts of the Muslim Knight, The Furusiyya Art Foundation Collection, Milan, 2008. 1.5 kg, 45.5cm (18"). From an important private family collection of arms and armour; acquired on the European art market in the 1980s, and thence by descent; believed originally from Eastern Europe; accompanied by an academic report by military specialist Dr Raffaele D'Amato. The war mace belongs to the group of the eastern war maces used by the Mongol armies in 13th century. In particular it is an interesting parallel to a mace published by Gorelik (1983, pl.27, n.67), having the same hexagonal prismatic shape, dated at the 13th century AD. It is also the same kind of mace that was brandished by the Il-Kh?nid Persian-Mongol warriors (scene of the battle of Ardashir and Artavan) in the very famous manuscript Demotte Sh?hn?mah, made in ?dharbayj?n in about 1335 AD (Nicolle, 1999, figs.632J"). The mace, perhaps because of its ancient associations, acquired a legendary quality, second only to the swords in the Islamic world, and therefore also of the Ilkhanid Turco-Mongol warlike state, that with the Sultan Ghazan adhered to the Islam in 1295 AD. Amongst Mongols and Turkish warriors, the mace became a symbol of office, and maces, gilded like this one, played a role in ceremonies which significance was a mixture of religious and military elements. From a military point of view, it was an extremely effective weapon in close combat, particularly from horseback against an armoured opponent, where a heavy mace could easily damage even the thickest steel armour and crash heads and helmets at the same time (Bashir, 2008, p.235"). The Ilkhanid Empire was originally part of the Mongol Empire founded by Genghis Khan, its Persian branch created by Hulegu, grandson of Genghis Khan himself. Settled in Persia, the Mongols fostered the growth of cosmopolitan cities with rich courts and wealthy patrons, who encouraged the arts to flourish. At the death of Kublai Khan the Ilkhanid Khanate was de facto independent, until his dissolution in 1335 AD. The core of its army were the powerful armoured cavalrymen, of Mongol, Turkish and Iranian origin, covered with Khuyagh armour, a lamellar or laminated corselet, mainly in iron, sometimes in bronze; they wore hemispherical helmets with reinforced brow, a plume tube or a spike, and mail, lamellar or leather aventail, round shields and offensive weapons like sabres, bow and arrows and naturally war maces (Heath, 1984, pp.114-115"). Most probably our specimen is from an excavation. The piece is very rare and is in excellent condition. The mace is a type of short-arms, a weapon of impact-crushing action, consisting of a wooden or metal handle (rod) and a spherical pommel (head), which can be smooth or studded with spikes. The mace is one of the oldest types of edged weapons, a direct heir to the club, which began to be used in the Stone Age. It became widespread in the late Middle Ages, which was due to the excellent 'armour-piercing' qualities of this weapon. The mace was great for breaking through heavy armour and helmets. The heads of some maces were huge. Mace has several significant advantages over bladed weapons. Firstly, a mace (like a hammer) never got stuck in enemy armour or shield, which often happened with a sword or a spear. With the help of maces, it was possible to completely deprive the enemy of the shield, inflicting several strong blows on it. In this case, either the shield broke, or its owner received a fracture of the limb. You can also add that the blows of the mace almost never slide off. Secondly, you can learn to use a mace much faster than a sword. In addition, these weapons were relatively cheap and almost 'unkillable'. The mace has a significant advantage in comparison with the war hammer: the enemy can be beaten with either side of the weapon. The mace was an essential weapon according the Islamic Fur?s?yah during close combat, and some military treatises are devoted to this weapon (for example, the 'Kit?b Ma?rifat La?b al-Dabb?s f? Awq?t al-?ur?b wa-al-?ir?? ?alá-al-Khayl,' held in Paris, BNF MS Ar. 2830 and BNF MS Ar. 6604; Istanbul, Ayasofya MS 3186; on the fur?s?yah treatises dealing with the art of the mace, see also al-Sarraf, 'Mamluk Fur?s?yah Literature and Its Antecedents'"). The most common name for the club/mace was the Persian 'gurz' and its derivatives: garz, horz and gargaz. The written sources describe four methods of conducting battle: throwing at an enemy from a long distance: close combat at a distance proportioned to the length of the club; rotation of the mace when a warrior was surrounded by enemies; defeating the enemy in front of you. The maces or clubs with huge heads and relatively short poles were suitable for throwing. Our mace belongs to a simplified form of maces, a sort of cube-shaped tops with six cut corners transforming it in hexagon (type II"). All the specimens are in iron and date back to the 12th14th centuries. A very widespread category of finds is made up of type II maces, mainly found in the excavations of the Southern Russian cities that were destroyed during the Tatar-Mongol invasion. They were also found in Novgorod, Moscow, and in the peasant Kostroma barrows. Usually, maces were considered to belong to the nobility, but the simpler specimens probably were widely available as weapons for ordinary soldiers, citizens and peasants. This is also supported by the simplicity and sometimes carelessness in the decoration of the maces themselves.
Preview:
Monday 25th November from 12 noon Champagne Reception 6pm - 9pm
Address:
23-24 Berkeley Square London, W1J 6HE United Kingdom
Start time:

Online payment is available,
You will be qualified after paid the deposit!

Online payment is available for this session.

Bidding for buyers is available,
please call us for further information. Our hot line is400-010-3636 !

This session is a live auction,
available for online bidding and reserved bidding