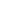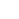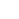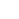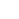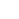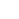LOT 433 Post Medieval Gold 'Fear God Above All' Posy Ring
Viewed 90 Frequency
Pre-bid 0 Frequency
 Collect
Collect
Name
Size
Description
Translation provided by Youdao
Mid 16th-early 18th century AD. A gold band ornamented with a circumferential frieze of oval bosses to the external face, faux ropework borders around, smaller domed pellets between to the top and bottom edges; the interior inscribed in italics: 'Fear god above all' in cursive script, partial remains of niello inlay, followed by stamped maker's mark 'IY[or V]' in rectangular cartouche, possibly that of John Young entered in 1760 and in use until at least 1793. Cf. The Portable Antiquities Scheme Database, id.NMS-B8BCC4; BERK-118101; LIN-B6F8A3; SOM-823925; SF-3A8B11, for very similar with different inscriptions dated c.1550-1700; See Oman (1974, plate 58 c, p. 111) for a very similar example with a different inscription, dated to the early 17th century; cf. The British Museum, museum number 1942,0708.1, for broadly similar, different inscription. 2.77 grams, 18.83mm overall, 15.44mm internal diameter (approximate size British I, USA 4 1/4, Europe 7.44, Japan 7) (3/4"). From the Albert Ward collection, Essex, UK; acquired on the UK antiques market between 1974-1985. Posy is derived from poesy or poetry. In the medieval period many rings bore posy inscriptions in Latin or French, the languages frequently spoken by the affluent elites. Later, inscriptions in English became more usual, although the lack of standardised spelling might surprise the modern reader. The inscription is generally found on the interior of the ring, hidden to everyone except the wearer and most of the sentimental mottoes were taken from the popular literature of the time. In fact, love inscriptions often repeat each other, which suggests that goldsmiths used stock phrases. In the later 16th century, posy specifically meant a short inscription. A posy is described in contemporary literature as a short epigram of less than one verse. George Puttenham (1589) explained that these phrases were not only inscribed on finger rings, but also applied to arms and trenchers. The practice of giving rings engraved with mottoes at betrothals or weddings was common in England from the 16th century onwards, and continued until the late 18th century. Sources suggest that rings could be acquired ready- engraved, or alternatively engraved sometime after their initial production, by a hand other than the goldsmiths. Joan Evans assumed that posy rings were principally used by/between lovers and distinguished four contexts for the giving of posy rings by one lover to another: betrothals, weddings, St Valentines Day and occasions of mourning. Samuel Pepys diary makes clear that posy rings might also mark the marriage of a family member, when bearers could even commission their own rings and chose their own mottoes from books. The rings could also function as tokens of friendship or loyalty. [A video of this lot is available to view on Timeline Auctions Website] [No Reserve] Condition Report Fair condition.
Preview:
Address:
London, LDN, UK
Start time:

Online payment is available,
You will be qualified after paid the deposit!

Online payment is available for this session.

Bidding for buyers is available,
please call us for further information. Our hot line is400-010-3636 !

This session is a live auction,
available for online bidding and reserved bidding